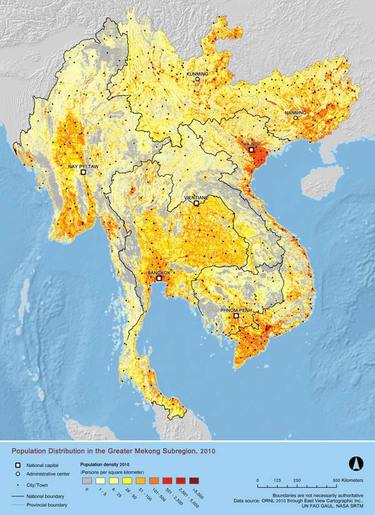
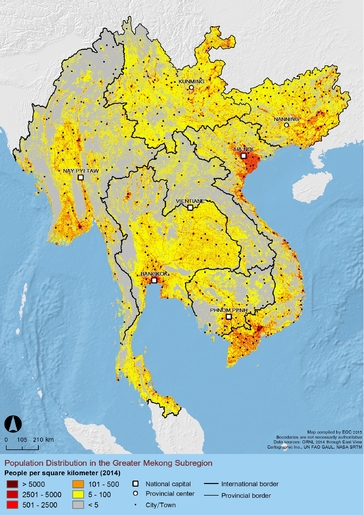
-
November 30, 2016ADB
Nature-Based Solutions for Building Resilience in Towns and Cities: Case Studies from the Greater Mekong Subregion
-
November 27, 2016UNDP
Guidance Note | Municipal Solid Waste Management in Crisis and Post-Crisis Setting
-
August 01, 2016Asian Development Bank
Greater Mekong Subregion Statistics on Growth, Infrastructure and Trade (Second Edition)
-
June 14, 2016ADB
ADB - Urban Development in the Greater Mekong Subregion
-
May 31, 2016UNEP, Global Infrastructure Basel (GIB)
Sustainable Infrastructure and Finance
-
July 14, 2015Grantham Research Institute on Climate Change and the Environment
Driving Sustainable Development Through Better Infrastructure: Key Elements of A Transformation Program
-
June 08, 2014GMS Core Environment Program
Final Report of Estimating Industrial Pollution using IPPS in Lao PDR
-
4th March 2018
Source: Viet Nam NewsHCM City plans infrastructure projects in 2018
-
3rd February 2018
Source: Vietnam NetADB helps urban infrastructure development in HCM City
-
1st February 2018
Source: ADBADB, China Everbright International Facilitate Clean Waste-to-Energy PPP in Viet Nam
-
24th January 2018
Source: Vientiane TimesLao PDR - Luang Prabang to receive Asean award for cleanliness
-
5th January 2018
Source: VietNamNet BridgeViet Nam - Air pollution at alarming rate in HCM City
-
4th January 2018
Source: VietNamNet BridgeViet Nam - The most significant environmental protection events in 2017
-
27th December 2017
Source: Vientiane TimesLao PDR - Govt vows to improve investment climate to drive growth
-
7th December 2017
Source: Ministry of Environmental ProtectionChina - UN concludes environmental assembly with pledges to end pollution
-
4th December 2017
Source: Ministry of Environmental ProtectionChina to improve green manufacturing standards system
-
3rd December 2017
Source: VietNamNet BridgeViet Nam - Will a carbon tax be imposed on coal-fired thermal power plants?
-
3rd December 2017
Source: Ministry of Environmental ProtectionChina - Beijing air pollution notably reduced in winter: Environment minister
-
28th November 2017
Source: VietNamNet BridgeViet Nam - Scientists oppose building of coal-fired power plants
-
28th November 2017
Source: The Voice of Viet NamViet Nam - Mekong Delta needs various financial resources to tackle climate change
-
25th November 2017
Source: VietNamNet BridgeViet Nam - Economic strategy must include natural disaster prevention
-
25th November 2017
Source: The NationMekong region cities ‘face same problems’
-
25th November 2017
Source: The NationPlanet Earth suffering from light pollution
-
23rd November 2017
Source: Ministry of Environmental ProtectionChina earmarks 7.5 billion dollars for environment protection
-
20th November 2017
Source: Tuoi Tre NewsViet Nam - Central Power Corporation operates electric cars, charging station in Da Nang
-
19th November 2017
Source: Ministry of Environmental ProtectionEnvironmental industries growing in China: Analysts
-
19th November 2017
Source: Eco-BusinessCOP23: Key outcomes agreed at the UN climate talks in Bonn
-
19th November 2017
Source: ADBADB, Lao PDR Sign Agreement to Enhance Sanitary, Phytosanitary Management Systems
-
18th November 2017
Source: VietNamNet BridgeViet Nam - Construction Ministry tasked with assessing coal ash treatment
-
16th November 2017
Source: Mekong EyeViet Nam - Rising coal prices cost Vietnam billions
-
16th November 2017
Source: Ministry of Environmental Protection1,140 officials held accountable over environmental damages
-
16th November 2017
Source: Eco-BusinessASEAN countries must act together to confront climate change
-
14th November 2017
Source: The NationWhich Asian country has suffered most financial loss due to ?climate ?change?
-
6th November 2017
Source: Ministry of Environmental ProtectionUN climate talks open in Bonn with call to uphold Paris Agreement path
-
1st November 2017
Source: ADBADB to Support Development of Green, Resilient Urban Infrastructure in Viet Nam's Secondary Cities
-
31st October 2017
Source: UNEAThe trucker and the vendor: Mapping gender to boost urban resilience in Laos
-
31st October 2017
Source: MizzimaMyanmar - $2.8 billion coal-fired power plant to be built in Kayin State
-
31st October 2017
Source: VietNamNet BridgeViet Nam - Target programme for climate change response and green growth approved
-
30th October 2017
Source: The GuardianUN warns of 'unacceptable' greenhouse gas emissions gap
-
30th October 2017
Source: National News Bureau of ThailandThailand - New legislation Smoke-Free along the beach
-
30th October 2017
Source: Ministry of Environmental ProtectionChina can lead the way on green governance, environmental lawyer says
-
29th October 2017
Source: The GuardianClimate change already bringing disease, air pollution and heatwaves
-
27th October 2017
Source: VietNamNet BridgeViet Nam - JICA helps HCM City monitor greenhouse gas emissions
-
27th October 2017
Source: VietNamNet BridgeVietnam to develop natural resources, environment monitoring database
-
25th October 2017
Source: Ministry of Environmental ProtectionChina fights uphill battle against air pollution
-
24th October 2017
Source: Vientiane TimesViet Nam - Titanium mining puts environment at stake
-
24th October 2017
Source: Vientiane TimesViet Nam - Hanoi to install additional 70 air monitoring stations
-
19th October 2017
Source: VietNamNet BridgeViet Nam - Green infrastructure: Solution to many urban problems
-
18th October 2017
Source: VietNamNet BridgeViet Nam - Ministry seeks higher budget for environmental protection
-
10th October 2017
Source: VietNamNet BridgeViet Nam - Air quality getting worse as legal loopholes still exists
-
3rd October 2017
Source: Myanmar TimesMyanmar - Burning coal chokes residents, pollutes river near Tanintharyi mine; government slow to respond
-
25th September 2017
Source: Khmer Times$64b GMS action plan
-
24th September 2017
Source: Ministry of Environmental Protection (MEP)China - Building ban to fight pollution
-
24th September 2017
Source: Viet Nam NewsViet Nam - Pollution from landfill a growing concern
-
23rd September 2017
Source: VietNamNet BridgeViet Nam - Aquatic plants suggested to purify polluted river water
-
22nd September 2017
Source: VietNamNet BridgeViet Nam - How environmental pollution is ruining the Mekong Delta
-
21st September 2017
Source: VietNamNet BridgeViet Nam - Legal loopholes make it impossible to control air quality
-
20th September 2017
Source: ADBNew ADB-Lao PDR Strategy to Support Inclusive, Sustainable Growth
-
20th September 2017
Source: Viet Nam NewsGMS ministerial meeting plans for future
-
13th September 2017
Source: CambodiaCambodia - Factories get environment checks
-
13th September 2017
Source: Ministry of Environmental Protection (MEP)China - Top court, UNEP sign MOU to deepen judicial co-op
-
12th September 2017
Source: The NationThailand - Two step forward as smart city pioneers
-
12th September 2017
Source: Lao News AgencyLaos, Thailand Ink Pollution Management Deal
-
12th September 2017
Source: ASEAN Secretariat News14th ASEAN Ministerial Meeting on the Environment and the 13th Meeting of the Conference of the Parties to the ASEAN Agreement on Transboundary Haze Pollution
-
10th September 2017
Source: The NationPongpipat follows Myanmar environmental regulations
-
10th September 2017
Source: VietNamNet BridgeViet Nam - Turning waste into electricity is a quick money-earner for investors
-
10th September 2017
Source: Ministry of Environmental ProtectionChina - Over half of firms in Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei region violating environmental rules
-
10th September 2017
Source: MongabayDeforestation in Cambodia linked to ill health in children
-
7th September 2017
Source: ADBMinisters Agree to Step Up Cooperation on Boosting Food Safety in Mekong
-
5th September 2017
Source: Ministry of Environmental ProtectionChina's strengthened pollution laws yield results
-
4th September 2017
Source: Yunnan Environmental Protection DepartmentNo environmental impact detected in China after DPRK nuclear test
-
1st September 2017
Source: VietNamNet BridgeViet Nam - Carbon market necessary to attain GHG reduction targets
-
27th August 2017
Source: VietNamNet BridgeViet Nam - Biologist warning on building paper mill
-
27th August 2017
Source: Ministry of Environmental Protection (MEP)China, South Korea and Japan vow to jointly tackle air pollution
-
27th August 2017
Source: Ministry of Environmental Protection (MEP)China - Air pollution targeted in 28 cities
-
23rd August 2017
Source: VietNamNet BridgeVietnam ranks 27th in greenhouse gas emissions
-
23rd August 2017
Source: MRCPromoting Sustainable Watershed Management in the Lower Mekong Basin
-
18th August 2017
Source: VietNamNet BridgeViet Nam - Vermicelli pollution no more
-
17th August 2017
Source: Yunnan Environmental Protection Department (YEPD)China moves to standardize recycling industry
-
16th August 2017
Source: Ministry of Environmental Protection (MEP)Chinese cities see fewer "good air" days in July
-
16th August 2017
Source: VietNamNet BridgeViet Nam - Coastal Da Nang faces severe pollution problems
-
14th August 2017
Source: Ministry of Environmental Protection (MEP)China reports uneven progress in reducing water pollution
-
13th August 2017
Source: VietNamNet BridgeViet Nam - Urbanites face health risks from air pollution
-
12th August 2017
Source: VietNamNet BridgeViet Nam - Overloaded landfill risks contaminating water supply
-
10th August 2017
Source: Ministry of Environmental Protection (MEP)Foreign waste import ban leaves Western nations, Chinese manufacturers in a dilemma
-
6th August 2017
Source: Ministry of Environmental Protection (MEP)China tightens pollution control with discharge permits
-
27th July 2017
Source: Ministry of Environmental Protection (MEP)China's planned ban on imported scrap vexes an industry
-
27th July 2017
Source: Ministry of Environmental Protection (MEP)China - Pollution action plan detailed
-
25th July 2017
Source: VietNamNet BridgeViet Nam - Binh Thuan coal plant mud dump to be repurposed
-
24th July 2017
Source: VietNamNet BridgeViet Nam - Large cities in Vietnam facing rising air pollution
-
23rd July 2017
Source: Yunnan Environmental Protection Department (YEPD)China - Severe pollution leads to discipline
-
23rd July 2017
Source: VietNamNet BridgeViet Nam - Vietnamese cities aim at waste-to-energy future
-
15th July 2017
Source: VietNamNet BridgeViet Nam - Power generator to pour 2.4 mil m3 of sludge into Binh Thuan sea
-
13th July 2017
Source: VietNamNet BridgeViet Nam - Thai Nguyen: uncontrolled mineral exploitation pushes locals to the wall
-
13th July 2017
Source: VietNamNet BridgeViet Nam - Major reservoir at risk of pollution
-
13th July 2017
Source: VietNamNet BridgeViet Nam - Da Nang to have first waste-to-electricity project
-
13th July 2017
Source: Eco-Business2016 was the deadliest year ever for environmental defenders
-
11th July 2017
Source: VietNamNet BridgeViet Nam - Hanoi air polluted by thermal power plants
-
9th July 2017
Source: Mekong EyeViet Nam - When will they learn? More power plant waste threatens marine reserve in central Vietnam
-
4th July 2017
Source: Ministry of Environmental Protection (MEP)Green zones to help fund fight against pollution
-
4th July 2017
Source: Ministry of Environmental Protection (MEP)China cracks down on pollution in imported waste processing
-
2nd July 2017
Source: VietNamNet BridgeViet Nam - Hue students discover material which can replace plastic bags
-
1st July 2017
Source: VN ExpressConcerns as Vietnam allows coal-fired power plant to dump waste near protected waters
-
30th June 2017
Source: VietNamNet BridgeViet Nam - Polluting factories still remain in Hanoi inner city
-
29th June 2017
Source: Ministry of Environmental Protection (MEP)China's inshore seawater quality improving
-
26th June 2017
Source: Ministry of Environmental Protection (MEP)China - Environmental projects expected to improve quality of life for city's residents
-
26th June 2017
Source: XinhuaNetChina revises law on water pollution prevention and control
-
25th June 2017
Source: VietNamNet BridgeIt’s time for biodegradable plastic bags in Vietnam
-
25th June 2017
Source: Ministry of Environmental Protection (MEP)China - BRICS pledges environment cooperation
-
25th June 2017
Source: Viet Nam NewsVN and Green Climate Fund co-operate on climate resilient development
-
23rd June 2017
Source: VietNamNet BridgeViet Nam - Hanoi works to tackle environmental pollution
-
22nd June 2017
Source: Eco-BusinessWaste management in Asia: 1 goal, 5 cities, 5 lessons
-
21st June 2017
Source: VietNamNet BridgeViet Nam - HCM City calls for private investment in waste water treatment
-
21st June 2017
Source: VietNamNet BridgeViet Nam - Tightened environmental protection at thermal power plants
-
21st June 2017
Source: Ministry of Environmental ProtectionChina unrolls nationwide soil pollution survey
-
21st June 2017
Source: Yunnan Environmental Protection DepartmentChina - Soil monitoring network passes milestone
-
20th June 2017
Source: VietNamNet BridgeViet Nam - Lam Dong: Environment watchdog issues fine of VND400 mln on polluter
-
18th June 2017
Source: Ministry of Environmental Protection (MEP)China's air quality worsens in May
-
14th June 2017
Source: VietNamNet BridgeViet Nam - Hanoi sets environmental protection goals
-
13th June 2017
Source: VietNamNet BridgeAir pollution in Vietnam threatens economic growth
-
12th June 2017
Source: VietNamNet BridgeViet Nam - HCM City vows to reduce waste landfill, replace with recycling
-
10th June 2017
Source: National News Bureau of ThailandThailand succeeds reducing greenhouse gas emission below limit
-
7th June 2017
Source: Ministry of Environmental ProtectionChina - Xi stresses clean energy development
-
6th June 2017
Source: Ministry of Environmental ProtectionChina - Straw recycling expo aims to cut rural air pollution
-
4th June 2017
Source: VietNamNet BridgeViet Nam - Central province restarts garbage treatment project
-
4th June 2017
Source: Myanmar TimesMyanmar - Investor-friendly environment and human capital essential for Myanmar’s success in the Belt and Road Initiative
-
1st June 2017
Source: VietNamNet BridgeViet Nam - Firm causes pollution in Thanh Hoa Province
-
31st May 2017
Source: Ministry of Environmental ProtectionChina - Xi stresses green development
-
31st May 2017
Source: Ministry of Environmental ProtectionChina finds widespread violations of environment rules
-
31st May 2017
Source: VietNamNet BridgeViet Nam - Sand mining destroying rivers in Central Highlands, causing landslides
-
29th May 2017
Source: VietNamNet BridgeMekong basin dams pose danger: Experts
-
29th May 2017
Source: VietNamNet BridgeViet Nam - Environmental tax hikes planned for HCFC, plastic bags
-
28th May 2017
Source: VietNamNet BridgeViet Nam - Severe erosion threatens Binh Thuan
-
28th May 2017
Source: ASEAN Sustainable Agrifood System (ASEASN SAS)Chemical is out! Cambodian agriculture pushes hard towards biological control agents for sustainability
-
25th May 2017
Source: MongabayVietnam makes a big push for coal, while pledging to curb emissions
-
25th May 2017
Source: Myanmar TimesMyanmar - Tanintharyi tourism committee seeks IFC infrastructure support
-
25th May 2017
Source: Myanmar TimesOil spill preventive measures for Myanmar-China pipelines urged
-
24th May 2017
Source: Ministry of Environmental ProtectionMinistry: China to set stricter rules to curb soil pollution
-
24th May 2017
Source: Ministry of Environmental ProtectionChina - Companies exposed for faking air pollution data
-
24th May 2017
Source: The NationThailand - Bangkok roads flooded following heavy overnight rains
-
24th May 2017
Source: VietNamNet BridgeViet Nam - Scourge of mass fish deaths strikes again
-
23rd May 2017
Source: VietNamNet BridgeViet Nam - Air quality management plan designed for Mekong Delta city
-
23rd May 2017
Source: Ministry of Environmental ProtectionChina - Yanchang blazes trail in carbon capture tech
-
22nd May 2017
Source: VietNamNet BridgeViet Nam - Air pollution challenges Vietnam’s socio-economic development
-
22nd May 2017
Source: Viet Nam NewsViet Nam - Hà N?i-based UN office gets top green buildings award
-
22nd May 2017
Source: Khmer TimesAirline tax to help clean up Cambodia
-
22nd May 2017
Source: Ministry of Environmental Protection (MEP)China stresses law enforcement on solid waste management
-
18th May 2017
Source: VietNamNet BridgeViet Nam - Mercury crosses border gates, affecting environment
-
18th May 2017
Source: VietNamNet BridgeViet Nam - Fishing in provinces affected by Formosa toxic spill mostly recovered
-
18th May 2017
Source: Viet Nam NewsViet Nam - D?u Ti?ng Reservoir sand mining suspended
-
16th May 2017
Source: Ministry of Environmental Protection (MEP)China - Air quality improves in Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei region in April
-
16th May 2017
Source: Ministry of Environmental Protection (MEP)China - Pollution from diesel vehicles worldwide underestimated by 50 percent: study
-
15th May 2017
Source: Viet Nam NewsViet Nam - Illegal sand mining in northern province continues despite ban
-
14th May 2017
Source: VietNamNet BridgeViet Nam - It’s time to have a law on controlling air pollution: experts
-
11th May 2017
Source: Viet Nam NewsViet Nam - Mass clam deaths reported in Kiên Giang
-
10th May 2017
Source: National News Bureau of ThailandThailand - BMA to proceed with On Nut waste facility revamp
-
10th May 2017
Source: Ministry of Environmental ProtectionChina - Sewer systems leave many newly built wastewater treatment plants with idle capacity
-
10th May 2017
Source: VietNamNet BridgeViet Nam - South Korean companies fined $15,000 for sewage violations
-
10th May 2017
Source: National News Bureau of Thailand (NNT)Thailand - Public hearing on waste-to-energy plant takes place in Phetchaburi
-
9th May 2017
Source: VietNamNet BridgeViet Nam - Experts warn of environmental incidents as only 10% of urban waste water treated
-
9th May 2017
Source: Ministry of Environmental ProtectionChina - Two-thirds of inspected firms violate environment rules
-
8th May 2017
Source: ADBGovernment, Development Partners Meet to Discuss Myanmar's Clean Energy Options
-
7th May 2017
Source: ADBAfter 50 years, Asian Development Bank looks ahead
-
7th May 2017
Source: ADBADB-Article: Infrastructure Development in Asia: 12 Things to Know
-
6th May 2017
Source: VietNamNet BridgeViet Nam - Environmental pollution: concerning issue in HCM City
-
5th May 2017
Source: Viet Nam NewsScrap steel imports threaten Viet Nam’s environment
-
4th May 2017
Source: VietNamNet BridgeViet Nam - Hanoi suffers increasingly harmful air quality
-
4th May 2017
Source: Ministry of Environmental Protection (MEP)Air pollution more than half of environmental complaints in China
-
4th May 2017
Source: Ministry of Environmental Protection (MEP)China to boost recycling industry for greener growth
-
4th May 2017
Source: MizzimaMyanmar coal plant growth could kill 280,000: Study
-
2nd May 2017
Source: The Phnom Penh PostCambodia - Floating homes set sail after alleged fish die-off
-
2nd May 2017
Source: National News Bureau of Thailand (NNT)Thailand - BMA examines waste water in canals in Lat Krabang
-
29th April 2017
Source: The NationThailand - Tonne of trash collected in clean-up at Hei Island in Phuket
-
27th April 2017
Source: Eco-BusinessCambodia makes first solar power play
-
26th April 2017
Source: VietNamNet BridgeVietnam charts course towards green economy
-
20th April 2017
Source: Viet Nam NewsViet Nam - MonRE to issue list of industries polluting environment
-
20th April 2017
Source: National News Bureau of Thailand (NNT)Thailand - MNRE pledges to reduce greenhouse emissions on Earth Day
-
16th April 2017
Source: National News Bureau of Thailand (NNT)Thailand - Alternative Energy Development and Efficiency Dept: 450 buildings join energy regulation
-
3rd April 2017
Source: VietNamNet BridgeViet Nam - Foreign paper factory admits to pollution in Mekong Delta
-
30th March 2017
Source: Khmer TimesCambodia - Atomic energy pact with Russia
-
30th March 2017
Source: Ministry of Environmental Protection (MEP)China - Recycling smartphones a challenge for users
-
30th March 2017
Source: VietNamNet BridgeViet Nam - The black canals in HCM City
-
29th March 2017
Source: National News Bureau of Thailand (NNT)Thailand - Chulalongkorn University installs air quality monitoring system in Nan Province
-
29th March 2017
Source: Eco-BusinessHow government and business can work together to build better cities
-
29th March 2017
Source: VietNamNet BridgeViet Nam - Polluted water killed fish in Thai Binh's river
-
28th March 2017
Source: Yunnan Environmental Protection Department (YEPD)China - Greener Beijing mapped out by 2030
-
27th March 2017
Source: Ministry of Environmental Protection (MEP)China - Beijing offers free green burials for the first time
-
27th March 2017
Source: Eco-BusinessHow green buildings can help achieve the Sustainable Development Goals
-
27th March 2017
Source: Eco-BusinessHow new technologies are shrinking wastewater’s hefty carbon footprint
-
27th March 2017
Source: Mekong EyeASIA’S FUTURE CITIES: New buds of growth for Yangon’s ‘green movement’
-
26th March 2017
Source: VietNamNet BridgeViet Nam - The green economy needs the right kind of FDI: gov't
-
26th March 2017
Source: Ministry of Environmental Protection (MEP)China's air quality worsens in first two months
-
26th March 2017
Source: The ConservationGreen chemistry is key to reducing waste and improving sustainablity
-
26th March 2017
Source: UNEPWorld green economy leaders look for ways to spark a new green revolution – and set a path to the 2030 Agenda
-
26th March 2017
Source: Ministry of Environmental Protection (MEP)China - MEP releases the developments in water pollution control
-
25th March 2017
Source: The NationThailand - Bangkok’s Earth Hour campaign a big success
-
25th March 2017
Source: The NationThailand - Fires in Myanmar blanket the far North in smog
-
22nd March 2017
Source: Ministry of Environmental Protection (MEP)China - Wastewater should be recognized as a valuable resource, UN says on World Water Day
-
22nd March 2017
Source: Eco-BusinessChina pollution haze linked to climate change
-
21st March 2017
Source: VietNamNet BridgeViet Nam - Solid, hazardous waste discharged, but little collected
-
21st March 2017
Source: Yunnan Environmental Protection Department (YEPD)China - Expert calls for water price overhaul
-
21st March 2017
Source: The NationThailand - Call for Thailand’s ‘unacceptable’ water pollution problem to be tackled
-
20th March 2017
Source: Ministry of Environmental Protection (MEP)China's water cleaner in 2016, but still short of expectation: official
-
20th March 2017
Source: Channel NewsAsiaASIA'S FUTURE CITIES: Can Bangkok’s ‘green lungs’ survive?
-
20th March 2017
Source: ADBADB-Article: What Does Climate Change Mean for Asia’s Future Infrastructure?
-
19th March 2017
Source: Ministry of Environmental Protection (MEP)China - Government inspection finds hundreds of environmental violations
-
19th March 2017
Source: Viet Nam NewsViet Nam - Dozens of service co-ops treat waste
-
19th March 2017
Source: Eco-BusinessFighting China's war on pollution
-
19th March 2017
Source: China DialogueChina takes another step to reduce coal-fired power
-
18th March 2017
Source: Bangkok PostMyanmar - The Dawei development dream left high and dry
-
16th March 2017
Source: National News Bureau of Thailand (NNT)Thailand - Bangkok authorities encourage citizens to join in Earth Hour 2017
-
15th March 2017
Source: The NationThais asked to honour Earth Hour and switch off
-
13th March 2017
Source: Ministry of Environmental Protection (MEP)China - Pollution liability insurance plan gets government push
-
13th March 2017
Source: The NationThailand - Flipping happy: Coin swallowing Thai turtle on the mend
-
13th March 2017
Source: Eco-BusinessCan Asia achieve zero emissions despite explosive urban growth?
-
12th March 2017
Source: VietNamNet BridgeViet Nam - Students use seafood waste to grow safe vegetables
-
12th March 2017
Source: Ministry of Natural Resources and EnvironmentViet Nam - Plastic bag-picking tour attracts foreign visitors
-
12th March 2017
Source: VietNamNet BridgeViet Nam - Broken pond polluted rivers, killed fish in Nghe An
-
9th March 2017
Source: Ministry of Environmental Protection (MEP)China on right path for addressing air pollution: minister
-
9th March 2017
Source: The Myanmar TimesMyanmar - Ministry aims at 1 million housing units by 2030
-
8th March 2017
Source: VietNamNet BridgeViet Nam - Hanoi's lakes cleaned up
-
8th March 2017
Source: Ministry of Environmental Protection (MEP)China - Minister: Air pollution probe finds 2,000 faults
-
6th March 2017
Source: Khmer TimesCambodia - Japan to help country go green
-
6th March 2017
Source: The Phnom Penh PostCambodia - JICA to aid impact studies
-
4th March 2017
Source: The NationThailand - Garbage danger warning as coin-eating turtle faces life-saving op
-
3rd March 2017
Source: The NationThailand - Saved turtles gifted US Embassy playground
-
2nd March 2017
Source: Viet Nam NewsViet Nam - Pollution: Ministry to inspect 520 facilities
-
28th February 2017
Source: The NationThailand - Activists urge authorities to stay neutral, open door for info-based debates
-
28th February 2017
Source: VietNamNet BridgeViet Nam - Hanoi vows to eliminate 2.5 million old, polluting motorbikes
-
28th February 2017
Source: VietNamNet BridgeViet Nam - Red streak in Vung Ang economic zone caused by algal bloom
-
27th February 2017
Source: ADBADB, Dynagreen, 10 Banks Partner to Boost Clean Waste-to-Energy PPP in PRC
-
27th February 2017
Source: Ministry of Environmental Protection (MEP)China - MEP holds a video conference on the deployments of the thematic inspection on air quality in Q1
-
26th February 2017
Source: The NationThailand - Fight against garbage in the ocean starts at individual level: Greenpeace
-
23rd February 2017
Source: National News Bureau of Thailand (NNT)Thailand - PCD organizes 6th MSC Mekong to tackle regional haze pollution
-
23rd February 2017
Source: ASEANASEAN sets priorities to address transboundary haze pollution in Mekong sub-region
-
22nd February 2017
Source: UNEPUN Declares War on Ocean Plastic
-
22nd February 2017
Source: Ministry of Environmental Protection (MEP)China - MEP releases the air quality status of key regions and 74 cities in January 2017
-
8th February 2017
Source: Ministry of Environmental Protection (MEP)China encourages environmentally friendly IPOs
-
26th January 2017
Source: VNExpressVietnam 2017: Prospects and challenges
-
25th January 2017
Source: VNExpressVietnam punishes four officials over Formosa environmental disaster
-
24th January 2017
Source: VietNamNet BridgeViet Nam - Hundreds of containers of waste abandoned at Saigon ports
-
24th January 2017
Source: Lao News AgencyLao PDR - Several Factories Closed in Vientiane Capital
-
24th January 2017
Source: China DialogueCan China meet its 2017 air quality goals?
-
23rd January 2017
Source: China Dialogue2017: What next for green finance?
-
23rd January 2017
Source: ADBADB Infographic - Data Show 50 Years of Changing Asia
-
22nd January 2017
Source: Ministry of Environmental Protection (MEP)China - Green bond rise seen as smog thickens
-
22nd January 2017
Source: Ministry of Environmental Protection (MEP)China - Hebei has 6 of 10 most polluted Chinese cities in 2016
-
22nd January 2017
Source: VietNamNet BridgeViet Nam - Polluted canals in HCM City emit bad odors, affect residents' lives
-
22nd January 2017
Source: National News Bureau of Thailand (NNT)Thailand - BMA initiates 1 Person 1 Bottle program to reduce waste at Sanam Luang
-
22nd January 2017
Source: Ministry of Environmental Protection (MEP)China - National Working Conference on Environmental Protection held in Beijing
-
19th January 2017
Source: Ministry of Environmental Protection (MEP)China's local governments prioritize pollution control in work reports
-
18th January 2017
Source: Ministry of Environmental Protection (MEP)China sets up lifelong accountability system to control soil pollution
-
17th January 2017
Source: Ministry of Environmental Protection (MEP)China to punish two enterprises for excessive pollution
-
17th January 2017
Source: VietNamNet BridgeViet Nam - 282 poor air quality days in capital in 2016
-
16th January 2017
Source: China DialogueChina - Why officials must fight against rivers polluted for profit
-
16th January 2017
Source: VietNamNet BridgeVietnam imports tons of carbendazim, a carcinogen
-
15th January 2017
Source: Ministry of Environmental Protection (MEP)China - Beijing to spend billions to tackle air pollution in 2017
-
15th January 2017
Source: Ministry of Environmental Protection (MEP)China Focus: China shows progress in environmental protection
-
15th January 2017
Source: CNNBeijing's smog: A tale of two cities
-
12th January 2017
Source: Ministry of Environmental Protection (MEP)Central China city to install air purifiers at all schools
-
12th January 2017
Source: Ministry of Environmental Protection (MEP)China - Environment experts look into high levels of sulfur in Linfen
-
12th January 2017
Source: VietNamNet BridgeViet Nam - Environmental highlights in 2016
-
12th January 2017
Source: VietNamNet BridgeViet Nam - Hanoi to set up garbage collection stations
-
11th January 2017
Source: Ministry of Environmental Protection (MEP)China - 720 people detained in environment inspections
-
10th January 2017
Source: Ministry of Environmental Protection (MEP)China - Over 1,300 companies punished in pollution-plagued Shanxi
-
10th January 2017
Source: VietNamNet BridgeViet Nam - Environmental standards to be tightened in 2017
-
10th January 2017
Source: Ministry of Natural Resources and Environment20 years of Vietnam's engagement in the ASEAN environmental cooperation
-
9th January 2017
Source: Ministry of Environmental Protection (MEP)China - Coal blamed for high SO2 levels
-
8th January 2017
Source: Ministry of Environmental Protection (MEP)China - Company fined for 2,700 tonnes of acid dumped in east China rivers
-
8th January 2017
Source: Ministry of Environmental Protection (MEP)China - Minister feels 'guilty' for air pollution
-
8th January 2017
Source: ADBADB News - ADB Operations Reach a Record $31.5 Billion in 2016
-
8th January 2017
Source: Viet Nam NewsViet Nam - Polluted water causes mass clam deaths in Thanh Hóa
-
5th January 2017
Source: Ministry of Environmental Protection (MEP)China - Tianjin: 500 electric buses hit roads in China's latest clean energy push
-
4th January 2017
Source: Ministry of Environmental Protection (MEP)China - 62 pct of Chinese cities plagued by air pollution
-
3rd January 2017
Source: Ministry of Environmental ProtectionChina to track second-hand vehicle emissions
-
3rd January 2017
Source: Ministry of Environmental ProtectionHeavy fog, smog continue to disrupt traffic in China
-
3rd January 2017
Source: VietNamNet BridgeViet Nam - Environmental issues a major concern among public in 2016
-
2nd January 2017
Source: Ministry of Environmental Protection24 Chinese cities on pollution red alert
-
27th December 2016
Source: Ministry of Environmental Protection (MEP)China - Experts call for ecological protection in urban planning
-
26th December 2016
Source: Viet Nam NewsViet Nam - Experts warn about environmental pollution’s impacts on GDP growth
-
22nd December 2016
Source: Ministry of Natural Resources and EnvironmentPromote the handling of dioxin contamination in Viet Nam
-
19th December 2016
Source: Ministry of Natural Resources and EnvironmentViet Nam held an international exhibition on environmental technologies and eco-products
-
12th December 2016
Source: ADBADB Approves Second Loan of €458 Million to Help PRC Improve Air Quality in Greater Beijing Area
-
11th December 2016
Source: The Myanmar TimesMyanmar - National environmental policy gets an update
-
30th October 2016
Source: Agence Kampuchea Presse (AKP)Cambodia Readying for Regional Clean Tourist City Contest
-
30th October 2016
Source: VietNamNet BridgeViet Nam - Water pollution dismissed as reason for fish deaths in Hanoi's lake
-
30th October 2016
Source: The Myanmar TimesMyanmar - Concerns for soil quality sparks Sagaing survey
-
26th October 2016
Source: Viet Nam NewsViet Nam - Mass fish deaths in Linh ?àm Lake
-
23rd October 2016
Source: VietNamNet BridgeViet Nam pledges greenhouse gas mitigation
-
20th October 2016
Source: Ministry of Environmental Protection (MEP)China - MEP releases air quality status of key regions and 74 cities in the first three quarters and September
-
20th October 2016
Source: Ministry of Environmental Protection (MEP)China - Tackling pollution a difficult test governments must pass
-
20th October 2016
Source: Viet Nam NewsViet Nam - Polluted water causes fish deaths in Bình Thu?n
-
19th October 2016
Source: The IndependentScientists accidentally turn pollution into renewable energy
-
18th October 2016
Source: VietNamNet BridgeViet Nam pledges completion of GHG mitigation commitments
-
17th October 2016
Source: VietNamNet BridgePollution causes big revenue losses for tourism in central Viet Nam
-
16th October 2016
Source: Viet Nam NewsHà N?i to install 20 new air-monitoring stations
-
16th October 2016
Source: Agence Kampuchea Presse (AKP)Cambodia Launches Behavioural Change Campaign on Plastic Bag Use
-
15th October 2016
Source: VietNamNet Bridge30,000 people die in VN every year because of air pollution
-
14th October 2016
Source: Viet Nam NewsDa Nang looks to PPP in waste water treatment
-
14th October 2016
Source: UNEPCountries agree to curb powerful greenhouse gases in largest climate breakthrough since Paris
-
13th October 2016
Source: Ministry of Environmental Protection (MEP)Beijing issues blue alert on air pollution
-
11th October 2016
Source: Ministry of Environmental Protect (MEP)China - MEP releases the outputs of the studies on Children Environmental Exposure Behavioral Models in China
-
11th October 2016
Source: VietNamNet BridgeViet Nam - Relocated factory could pollute Da Nang’s water
-
9th October 2016
Source: Viet Nam NewsViet Nam - Waste water discharged into Nha Trang Bay monitored
-
9th October 2016
Source: National News Bureau of Thailand (NNT)Thailand - Pollution Control Dept to find out cause of deaths of stingrays in Samut Songkram
-
8th October 2016
Source: Ministry of Environmental ProtectionChina - MEP makes plans overnight to address heavy air pollution
-
2nd October 2016
Source: VietNamNet BridgeTonnes of fish die in Hanoi's West Lake
-
2nd October 2016
Source: The NationRenewable energy gains offer us a cleaner future
-
1st October 2016
Source: VietNamNet BridgeAir pollution in Hanoi, HCM City remains high
-
29th September 2016
Source: The Myanmar TimesMyanmar’s air pollution among the worst in the world: WHO
-
26th September 2016
Source: Climate CentralEarth’s CO2 Passes the 400 PPM Threshold—Maybe Permanently
-
25th September 2016
Source: WHOWHO releases country estimates on air pollution exposure and health impact
-
15th September 2016
Source: GMS-EOCADB: GMS e-Newsletter May-August 2016
-
11th September 2016
Source: China DailyChina and ASEAN countries make progress towards smart cities
-
9th September 2016
Source: Vientiane TimesLao PDR - Temples lead the way in creating green spaces
-
4th September 2016
Source: VietNamNet BridgeScientists: Chinese exports polluting Viet Nam through Red River
-
4th September 2016
Source: Mekong EyeGigawatts for Gigaspenders: Infographic shows Bangkok’s luxury malls use more energy than some provinces
-
3rd September 2016
Source: VietNamNet BridgeViet Nam commits to green growth
-
2nd September 2016
Source: China DailyChina - Innovations help lower emissions
-
2nd September 2016
Source: VietNamNet BridgeExperts: Damming places Mekong Delta in peril
-
2nd September 2016
Source: The Phnom Penh PostProtecting Cambodia’s island paradise?
-
30th August 2016
Source: XinhuaChina to establish green financing mechanism for greener growth
-
29th August 2016
Source: The Climate and Clean Air CoalitionBetter Air Quality Conference Opens in Busan, Korea: Warns Asia's Air Pollution Crisis Set to Get Worse Before it Gets Better
-
29th August 2016
Source: XinhuaChina sets stricter standards for pollutant discharge
-
24th August 2016
Source: VietNamNet BridgeHCM City to invest $3 million to build four air monitoring stations
-
21st August 2016
Source: Ministry of Natural Resources and Environment'Green Business' - a key for sustainable tourism development in Viet Nam
-
21st August 2016
Source: China DailyOfficials punished for neglect of pollution
-
16th August 2016
Source: XinhuaApple goes green, company commits to zero environmental waste in China
-
14th August 2016
Source: ADBADB Photo Contest Winners Focus on Actions to Protect Environment in PRC
-
14th August 2016
Source: XinhuaChina Focus: More polluters punished as prosecutors take action
-
12th August 2016
Source: XinhuaChina to step up support for green sector: top economic planner
-
11th August 2016
Source: GMS-EOCCambodia reviews its draft national environment strategy
-
1st August 2016
Source: Viet Nam NewsViet Nam - Formosa faces new waste penalties
-
31st July 2016
Source: National News Bureau of Thailand (NNT)Thailand - Treasury Department renovating Benjakitti park as a forest park for the Bangkok public
-
28th July 2016
Source: WWFThailand’s Tiger Temple Raid Highlights Need to Close Tiger Farms in Asia
-
28th July 2016
Source: Viet Nam NewsViet Nam - MoNRE to inspect wastewater nationwide
-
15th November 2015
Source: ADBADB News Release: ADB Loan to Boost Urban Services in Towns Along GMS Economic Corridor
-
5th May 2015
Source: ADBADB Video: Making Cities Climate Change Resilient
-
5th May 2015
Source: ADBADB: Climate Change Resilience in Asia's Cities