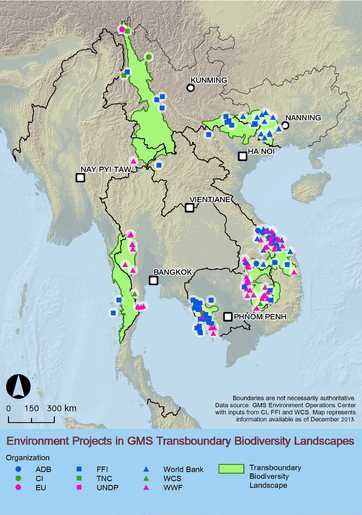
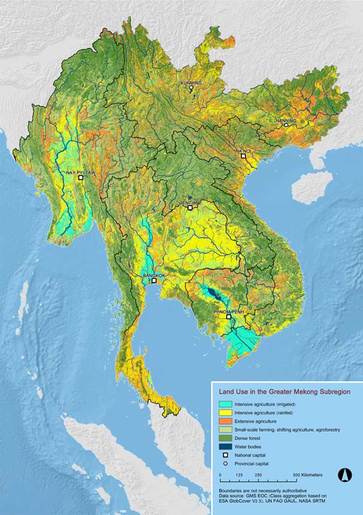
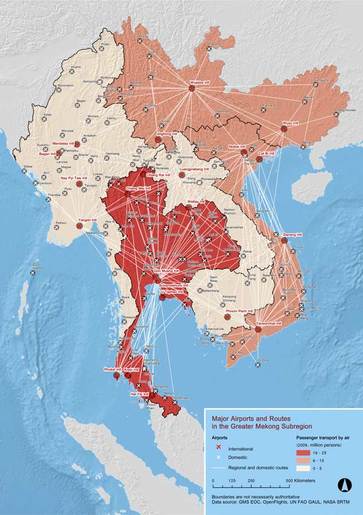
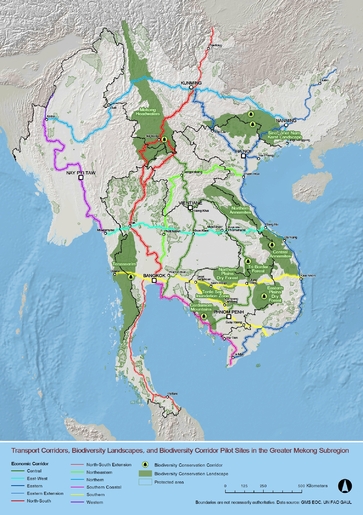
-
February 28, 2018IOP Science
Greenhouse gas emissions of hydropower in the Mekong River Basin
-
November 30, 2017GGGI
Green Energy Development Technical Guidelines 4th
-
November 30, 2017World Resources Institute
Roots of Prosperity: The Economics and Finance of Restoring Land
-
October 31, 2017UNEP
The Emissions Gap Report 2017: A UNEP synthesis report
-
October 31, 2017WB
State and Trends of Carbon Pricing 2017
-
October 31, 2017International Energy Agency
Technology Roadmap: Delivering Sustainable Bioenergy
-
October 09, 2017UNESCAP
Asia-Pacific Disaster Report 2017
-
September 30, 2017FAO
2017 Forest change in the Greater Mekong Subregion (GMS)
-
September 30, 2017Climate Focus
How Improved Land Use Can Contribute to the 1.5°C Goal of the Paris Agreement
-
September 27, 2017UNEA
Towards a pollution-free planet: Background report
-
September 07, 2017UNESCAP
Gender, the Environment and Sustainable Development in Asia and the Pacific
-
August 31, 2017ADB
Key Indicators for Asia and the Pacific 2017
-
August 31, 2017ADB
Trade Facilitation and Better Connectivity for an Inclusive Asia and Pacific
-
August 31, 2017ADB
Improving Lives of Rural Communities Through Developing Small Hybrid Renewable Energy Systems
-
August 31, 2017Frankfurt School-UNEP Collaborating Centre
Climate Metrics for Debt and Equity Portfolios: A Framework for Analysis
-
July 31, 2017ADB
Climate Change Operational Framework 2017–2030: Enhanced Actions for Low Greenhouse Gas Emissions and Climate-Resilient Development
-
July 31, 2017ADB
Catalyzing Green Finance: A Concept for Leveraging Blended Finance for Green Development
-
July 31, 2017RECOFTC
Moving from information dissemination to community participation in forest landscapes: How development organizations in Asia and the Pacific are using participatory development communication approaches
-
July 25, 2017UNESCAP
Regional Road Map for Implementing the 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development in Asia and the Pacific
-
July 09, 2017UNESCAP
Statistical Yearbook for Asia and the Pacific 2016: SDG Baseline Report
-
June 30, 2017ADB
A Region at Risk: The Human Dimensions of Climate Change in Asia and the Pacific
-
June 30, 2017UNEP
Green Finance Progress Report 2017
-
June 29, 2017the Stimson Center’s Southeast Asia
Mekong Power Shift: Emerging Trends in the GMS Power Sector
-
May 31, 2017ADB
Lessons from ADB Transport Projects: Moving Goods, Connecting People, and Disseminating Knowledge
-
May 31, 2017IUCN
Guidelines for tourism partnerships and concessions for protected areas: Generating sustainable revenues for conservation and development
-
May 15, 2017EcoAgriculture Partners, IUCN
Business for Sustainable Landscapes
-
May 11, 2017UNEP
Green Technology Choices: The Environmental and Resource Implications of Low-Carbon Technologies
-
May 01, 2017UNEA
UN Environment's Freshwater Strategy 2017 – 2021
-
April 30, 2017ADB
Banking on the Future of Asia and the Pacific: 50 Years of The Asian Development Bank
-
April 30, 2017ADB
Financing Asian Irrigation: Choices Before Us
-
April 30, 2017ADB
Risk Financing for Rural Climate Resilience in the Greater Mekong Subregion
-
April 30, 2017WB
Results-Based Climate Finance in Practice: Delivering Climate Finance for Low-Carbon Development
-
April 23, 2017SEI
SEI Annual Report 2016
-
April 05, 2017Frankfurt School-UNEP Collaborating Centre
Global Trends in Renewable Energy Investment 2017
-
March 31, 2017ADB
Asian Development Outlook (ADO) 2017: Transcending the Middle-Income Challenge
-
March 31, 2017ADB
Clean Energy Financing Partnership Facility: Annual Report 2016
-
March 31, 2017FAO
Agroforestry in rice production landscapes in Southeast Asia: A practical manual
-
March 31, 2017OECD
Climate-Resilient Infrastructure: Getting the Policies Right
-
March 26, 2017Mekong Partnership for the Environment
Guidelines on Public Participation in EIA in the Mekong Region
-
February 28, 2017ADB
Earth Observation for a Transforming Asia and Pacific
-
February 28, 2017ADB
Eradicating Poverty and Promoting Prosperity
-
February 28, 2017UNEP
Resource Efficiency: Potential and Economic Implications
-
February 28, 2017Mekong Institute
BASELINE SURVEY REPORT: Enhancing Competitiveness of Small and Medium-Sized Enterprises In The Southern Economic Corridor of ASEAN Mekong Sub-Region (AMS)
-
February 28, 2017ADB
Economics of Climate Change Mitigation in Central and West Asia
-
February 27, 2017ADB
The Long Road Ahead: Status Report on the Implementation of the ASEAN Mutual Recognition Arrangements on Professional Services
-
February 21, 2017ADB
Safeguarding the Rights of Asian Migrant Workers from Home to the Workplace
-
February 14, 2017FiBL & IFOAM - ORGANICS INTERNATIONAL
The World of Organic Agriculture 2017
-
January 31, 2017RECOFTC
Social forestry and climate change in the ASEAN region
-
January 31, 2017ADB
Energy Storage in Grids with High Penetration of Variable Generation
-
January 31, 2017FAO
FAO and the SDGs
-
January 31, 2017FAO
FAO's strategic work to enable inclusive and efficient agricultural and food systems
-
January 31, 2017FAO
Strategic work of FAO for Sustainable Food and Agriculture
-
January 31, 2017World Resources Institute
Attracting Private Investment to Landscape Restoration: A Roadmap
-
January 22, 2017EcoAgriculture Partners
Public Policy Guidelines for Integrated Landscape Management
-
January 18, 2017ASEAN
Investing in ASEAN 2017
-
January 12, 2017UNDP
UNDP's Response to El Nino and La Nina: From recurring crisis to resilience
-
December 31, 2016International Organization for Migration (IOM)
Assessing the Climate Change Environmental Degradation and Migration Nexus in South Asia
-
December 31, 2016CIFOR
CIFOR Priorities 2017: Advancing research for forests and people
-
December 31, 2016FAO
Strategic Work of FAO to Increase the Resilience of Livelihoods
-
December 31, 2016Biodiversity International
Creating mutual benefits: examples of gender and biodiversity outcomes from Bioversity International’s research
-
December 31, 2016FAO
Guide for planning, construction and maintenance of forest roads
-
December 31, 2016Mekong Business Initiative
2016 Mekong Business Initiative (MBI) Annual Report
-
December 18, 2016UNEP
Transboundary Lakes and Reservoirs: Status and Future Trends (Volume 2)
-
December 14, 2016ADB
Asian Economic Integration Report 2016
-
December 06, 2016UNDP
Delivering Sustainable Energy in a Changing Climate: Strategy Note on Sustainable Energy
-
December 05, 2016UNDP
BIOFIN Workbook: Mobilizing Resources for Biodiversity and Sustainable Development
-
November 30, 2016UNEP
The Rise Of Environmental Crime: A Growing Threat To Natural Resources, Peace, Development and Security
-
November 30, 2016FAO
State of the World's Forests 2016 - Forests and agriculture: land-use challenges and opportunities
-
November 30, 2016CIFOR
CIFOR Strategy 2016 – 2025: Stepping up to the new climate and development agenda
-
November 30, 2016FAO
The State of Food and Agriculture 2016 (SOFA): Climate change, agriculture and food security
-
November 30, 2016Bioversity International
Tropical Fruit Tree Diversity: Good Practices for Insitu and On-Farm Conservation
-
November 30, 2016ADB
Nature-Based Solutions for Building Resilience in Towns and Cities: Case Studies from the Greater Mekong Subregion
-
November 27, 2016UNDP
Guidance Note | Municipal Solid Waste Management in Crisis and Post-Crisis Setting
-
November 14, 2016UNDP
From MDGs to Sustainable Development For All: Lessons from 15 Years of Practice
-
November 10, 2016WWF
The Mekong River in the Economy Report
-
November 08, 2016UNDP
Transitioning from the MDGs to the SDGs
-
November 01, 2016UNDP
Adaptive Farms, Resilient Tables: Building secure food systems and celebrating distinct culinary traditions in a world of climate uncertainty
-
October 31, 2016GIZ
Advancing nationally determined contributions (NDCs) through climate-friendly refrigeration and air-conditioning
-
October 31, 2016World Agroforestry Centre (ICRAF)
Integrated systems research for sustainable smallholder agriculture in the Central Mekong
-
October 31, 2016German Development Institute (DIE)
Green Finance: Actors, challenges and policy recommendations
-
October 09, 2016ASEAN
ASEAN Strategic Plan for Culture and Arts 2016 – 2025
-
September 30, 2016ADB
ADB - Disaster Risk in Asia and the Pacific: Assessment, Management and Finance
-
September 14, 2016ADB
Asian Development Outlook 2016 Update: Meeting the Low-Carbon Growth Challenge
-
September 12, 2016ASEAN
Master Plan on ASEAN Connectivity 2025
-
September 08, 2016Tropenbos International and EcoAgriculture Partners
Guidelines-Participatory Planning, Monitoring and Evaluation of Multistakeholder Platforms in Integrated Landscape Initiatives
-
August 31, 2016Mekong Institute
Mekong Development Report 2016
-
August 01, 2016Asian Development Bank
Greater Mekong Subregion Statistics on Growth, Infrastructure and Trade (Second Edition)
-
July 16, 2016UNEP
Food Systems and Natural Resources
-
July 14, 2016Asian Development Bank
ADB - Natural Capital and the Rule of Law: Proceedings of the ADB Second Asian Judges Symposium on Environment 2013
-
June 30, 2016UNEP
Unlocking the Sustainable Potential Of Land Resources Evaluation Systems, Strategies and Tools
-
June 30, 2016Climate Focus
Fostering Climate Action through Trade-Related Policy Instruments Final report: Delivery strategies and support tools
-
June 16, 2016Ke Ai Advancing Research Evolving Science
Approaches to low carbon development in China and India
-
June 14, 2016ADB
ADB - Urban Development in the Greater Mekong Subregion
-
June 14, 2016Sciences Po and IOM
The State of Environmental Migration 2015 – A review of 2014
-
June 14, 2016ESCAP, IOM, ILO, OCHA, UN Women, UNAIDS, UNDP, UNFPA, UNHCR, UN-ACI, UNICEF, UNODC, WHO, World Bank
Asia-Pacific Migration Report 2015
-
June 14, 2016UNDP
Integrated Planning and Sustainable Development: Challenges and Opportunities
-
May 31, 2016FAO
Principles for the assessment of livestock impacts on biodiversity. Version 1
-
May 31, 2016UNEP, Global Infrastructure Basel (GIB)
Sustainable Infrastructure and Finance
-
May 31, 2016International Energy Agency
Next Generation Wind and Solar Power
-
May 30, 2016UNDP
2015 UNDP-GEF Annual Performance Report
-
May 17, 2016UNEP
The Open Ocean: Status and Trends: Summary for policy makers (Volume 5)
-
April 30, 2016RECOFTC
Community forestry-based climate change adaptation: A practitioner’s brief
-
April 30, 2016RECOFTC
Forests and climate change after Paris: An Asia-Pacific perspective
-
April 30, 2016IGES
Strengthening EIA in Asia
-
April 30, 2016IISD
State of Sustainability Initiatives Review: Standards and the Blue Economy
-
April 30, 2016UNEP
Green Finance and Developing Countries: Needs, Concerns and Innovations
-
April 12, 2016Asian Development Bank
ASEAN–ADB Cooperation Toward the ASEAN Community
-
March 31, 2016RECOFTC
Forest landscape restoration for Asia-Pacific forests
-
March 22, 2016IUCN
A global standard for the identification of Key Biodiversity Areas
-
February 29, 2016UNEP
Natural Capital Assessments at the National and Sub-National level: A Guide for Environmental Practitioners
-
January 14, 2016UNEP
Large Marine Ecosystems: Status and Trends: Summary for policy makers (Volume 4)
-
January 14, 2016UNEP
Transboundary Aquifers and Groundwater Systems of Small Island Developing States: Status and Trends: Summary for policy makers (Volume 1)
-
January 14, 2016UNEP
Transboundary river basins: Status and trends: Summary for policy makers (Volume 3)
-
January 12, 2016MRC
MRC: 20 Years of C20 Yearso of Coooperaption eration
-
January 11, 2016Asian Development Bank
Southeast Asia and the Economics of Global Climate Stabilization
-
December 31, 2015RECOFTC
The role of community forestry in climate change adaptation in the ASEAN region
-
December 31, 2015Mekong Institute
Mekong Institute: Strategic Plan 2016-2020
-
December 31, 2015FAO
Towards the implementation of the SSF Guidelines in the Southeast Asia region
-
December 03, 2015EcoAgriculture Partners
Landscape Partnerships for Sustainable Development: Achieving the SDGs through Integrated Landscape Management
-
November 30, 2015International Organization for Migration (IOM)
Migration Initiatives 2016
-
November 30, 2015ADB
Asian Economic Integration Report 2015: How Can Special Economic Zones Catalyze Economic Development?
-
November 29, 2015UNEP
Green Energy Choices: The benefits, risks and trade-offs of low-carbon technologies for electricity production
-
November 17, 2015Oxfam
Working Paper on Economic, Environmental and Social Impacts of Hydropower Development Lower Mekong Basin
-
November 10, 2015GMS Core Environment Program
Investing in Natural Capital for a Sustainable Future in the Greater Mekong Subregion
-
October 31, 2015IGES
The Paris Climate Agreement and Beyond: Linking Short-term Climate Actions to Long-term Goals
-
September 15, 2015Asian Development Bank
Regional Investment Framework Implementation Plan - First Progress Report
-
September 13, 2015Asian Development Bank
Economic Analysis of Climate-Proofing Investment Projects
-
September 09, 2015Asian Development Bank
Greater Mekong Subregion Urban Development Strategic Framework 2015 – 2022
-
September 09, 2015ADB
Greater Mekong Subregion Statistics On Growth, Connectivity and Sustainable Development (First Edition)
-
August 31, 2015IGES
Achieving the Sustainable Development Goals: From Agenda to Action
-
August 18, 2015PACT
Environmental Impact Assessment Comparative Analysis In Lower Mekong Countries
-
July 23, 2015Asian Development Bank
Renewable Energy Developments and Potential for the Greater Mekong Subregion
-
July 14, 2015Grantham Research Institute on Climate Change and the Environment
Driving Sustainable Development Through Better Infrastructure: Key Elements of A Transformation Program
-
June 30, 2015IGES
Greening Integration in Asia: How Regional Integration Can Benefit People and the Environment
-
May 31, 2015United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP)
Economic Valuation Of Wastewater: The Cost Of Action And The Cost Of No Action
-
April 30, 2015World Resources Institute
Scaling up Regreening: Six Steps to Success
-
April 14, 2015GMS Core Environment Program
Strategic Environmental Assessment in the Greater Mekong Subregion
-
April 14, 2015GMS Core Environment Program
Green Freight in the Greater Mekong Subregion
-
April 14, 2015GMS Core Environment Program
Ecosystem-based Approaches to Address Climate Change Challenges in the Greater Mekong Subregion
-
March 31, 2015ASEAN
Promotion of Climate Resilience for Food Security in ASEAN
-
March 26, 2015FAO
Developing an Environmental Monitoring System to Strengthen Fisheries and Aquaculture Resilience and Improve Early Warning in the Lower Mekong Basin
-
February 28, 2015Grantham Research Institute on Climate Change and the Environment, GGGI
Looking for Green Jobs: The impact of green growth on employment
-
January 01, 2015Asian Development Bank
Greater Mekong Subregion Regional Investment Framework Implementation Plan (2014-2018)
-
December 31, 2014CIAT, CGIAR, CCAFS
Towards climate resilience in agriculture for Southeast Asia: An overview for decision-makers
-
November 10, 2014EcoAgriculture Partners
Spatial Planning and Monitoring of Landscape Interventions: Maps to Link People with their Landscapes
-
November 10, 2014EcoAgriculture Partners
Ground-Based Photo-Monitoring of Landscape Changes Arising from Sustainable Land Management Practices
-
November 10, 2014OECD
Towards Green Growth in Southeast Asia
-
November 06, 2014Asian Development Bank
Climate Risk Management in ADB Projects
-
October 31, 2014EcoAgriculture Partners
A Landscape Perspective on Monitoring & Evaluation for Sustainable Land Management
-
August 07, 2014
Green Freight and Logistics in Asia: Delivering the Goods, Protecting the Environment
-
July 31, 2014UNEP
Towards a Global Map of Natural Capital - Key Ecosystem Assets
-
June 23, 2014Asian Development Bank
ADB Environmental Issues, Climate Changes, and Energy Security in Developing Asia
-
June 14, 2014Stockholm Environment Institute (SEI)
Climate Risks, Regional Integration, and Sustainability in the Mekong Region
-
June 10, 2014Asian Development Bank
ADB Clean Energy Investments Project Summaries
-
May 31, 2014ICEM
Natural Systems and Climate Change Resilience in the Lower Mekong Basin
-
May 28, 2014GMS Core Environment Program
Climate Change and Rural Communities in the Greater Mekong Subregion: A Framework for Assessing Vulnerability and Adaptation Options
-
May 27, 2014Asian Development Bank
ADB and Climate Investment Funds: Innovation and Action on Climate Change in Asia and the Pacific
-
May 20, 2014Asian Development Bank
The Environments of the Poor in Southeast Asia, East Asia and the Pacific
-
April 24, 2014SANDEE
Policy Brief: Operationalizing Environmental Economic National Accounts
-
April 14, 2014Asian Development Bank
Assessing Impact in the Greater Mekong Subregion: An Analysis of Regional Cooperation Projects
-
January 23, 2014UNEP
Building Natural Capital: How REDD+ Can Support A Green Economy
-
January 23, 2014UNEP
ASSESSING GLOBAL LAND USE: Balancing Consumption With Sustainable Supply
-
November 30, 2013Friedrich Ebert Stiftung
Green Growth Strategies in Asia: Drivers and Political Entry Points
-
November 27, 2013GMS Core Environment Program
Planning Sustainable Investments in the Greater Mekong Subregion
-
November 19, 2013WWF
Heart of Borneo: Investing in Nature for a Green Economy
-
October 31, 2013Asian Development Bank
Energy Outlook for Asia and the Pacific
-
October 13, 2013Asian Development Bank
ADB Environment Operational Directions 2013 – 2020
-
September 04, 2013Asian Development Bank
Prospects for Carbon Capture and Storage in Southeast Asia
-
June 30, 2013AfDB, OECD, UN and WB
A Toolkit of Policy Options to Support Inclusive Green Growth
-
April 16, 2013Asian Development Bank
ADB Report on Facilitating Safe Labor Migration in the Greater Mekong Subregion
-
December 11, 2012Asian Development Bank
GMS Atlas of the Environment - 2nd Edition
-
September 13, 2012Asian Development Bank
GMS: 20 Years of Partnership
-
August 31, 2012WB
Strategic Environmental Assessment in the World Bank: Learning from Recent Experience and Challenges
-
August 20, 2012Asian Development Bank
Agricultural Trade Facilitation in the Greater Mekong Subregion
-
June 14, 2012IUCN
Situation Analysis on Climate Change
-
May 31, 2012UNEP
Promoting Upstream-downstream Linkages Through Integrated Ecosystem Management in the Greater Mekong Subregion (UNEP Policy Series)